 |
|
 |
Types of wind rotors
Starting from classical horizontal axis rotors (old windmills), a lot of types of wind rotors were developed as time went on, some of them were excellent. Indeed the first windmills developed in Mesopotamia were built with vertical axis, mounting, radially, some vertical flags. After some centuries and thanks to the deep experience gained, man optimized the rotor reaching excellent results such as the Dutch and Greek windmills.
Wind rotors can be divided into three main groups:
- With horizontal axis
- With vertical axis
- Hybrid
Moreover, wind rotors can be classified into:
RESISTANCE SYSTEMS: where the blade offers resistance to the wind which presses on it making it move and generating mechanical energy.
LIFT SYSTEMS: where the blade, of aerodynamic form, exploits the lift principle, i.e. the air flow (wind) which allows it to move generating mechanical energy.

SYSTEM WITH HORIZONTAL AXIS
In this case the axis is perpendicular to the wind direction and the blades move to the direction of the air flux. The SAVONIUS rotor (from the name of the Finlander J. Savonius who invented it in 1929) is the simplest type. It can be built opposing two half cylinders hinged on the axis of the rotor itself. In this type of rotor a system of orientation of the blades is not necessary, however not all the surface is exposed to the wind. In fact, while a blade collects the air flux and it is pushed, the other one turns to the opposite side, reducing the performance.
The main characteristics of this wind rotor are the following ones:
• front area totally used
• high speed of rotation
• high coefficient of lift
• high power obtainable
Thanks to the high speed of rotation granted by this rotor, the complete system is very simple to be built and to be joined to the electrical generators. However, the propeller demands a refined technology as it has to grant lightness and strength. Moreover, the propeller generator could create some problems: small mistakes in its construction can destroy the whole system, tower included. This is why it is better to keep the turns number low and constant through brakes or aerodynamic solutions of different types.
|
|
 |
SYSTEM WITH VERTICAL AXIS
In this case the axis is perpendicular to the wind direction and the blades move to the direction of the air flux. The SAVONIUS rotor (from the name of the Finlander J. Savonius who invented it in 1929) is the simplest type. It can be built opposing two half cylinders hinged on the axis of the rotor itself. In this type of rotor a system of orientation of the blades is not necessary, however not all the surface is exposed to the wind. In fact, while a blade collects the air flux and it is pushed, the other one turns to the opposite side, reducing the performance.
The main characteristics of this wind rotor are the following ones:
• low speed of rotation
• high mechanical torque
• modest performance
There is also an aerodynamic limit which prevents to improve, beyond a certain level, the efficiency of the Savonius rotors. They are proper to mechanical uses as the water pumps. Indeed they are mostly used in rural areas.
|
|
 |
HYBRID SYSTEMS
They are the youngest and they combine the advantageous characteristics of both the systems with horizontal and vertical axis. In general they are with vertical axis with propellers or blades derived from the previous ones. Here are some examples: the Darrieous rotor, the Cycloturbine, the Ropatec rotor, the rotor with delta flange (see the photo), ext.
The main characteristics of this wind rotor are the following ones:
• easiness of construction
• high speed of rotation
• no orientation system
• power coefficients close to the theoretical value
|
|
 |
|
| |
» Types of wind rotors
|
|
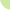 |
|
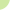 |
|
